Affecting about one of every hundred people, absence seizures (also known as "petit mal seizures") are caused when abnormal and excessive electrical activity in the central nervous system occurs. Normally, the neurons in the central nervous system communicate with each other by firing tiny electrical impulses.
A variety of causes can result in an absence seizure. The most common is misalignment of the central nervous system. Other causes include stroke, head trauma, tumors, and brain injury.
There are several ways to tell if you have a seizure. The first is if you experience a sudden onset of brief, intense symptoms including nausea, vomiting, sweating, and shaking or discomfort in the arm or leg. The symptoms may occur more than once.
Seizures occur in one or both hemispheres of your brain
The severity of the symptoms will determine the type of seizure you have. Some common types of seizures include focal epilepsy, which affect one side of the brain and is usually characterized by a single episode of seizures; mixed epilepsy, which affect both sides of your brain; and partial seizures, which occur only on one side of the body. Your physician can help you decide which type you have.
Seizures often do not cause serious problems, although they can be disturbing and frightening. For example, during a full seizure, you may experience lightheadedness, fainting, and nausea. A person experiencing a partial seizure, however, may experience difficulty breathing, nausea, vomiting, and numbness in the hand or feet.
Seizures often occur in a person without warning. However, it is possible for them to be provoked by certain situations, such as stress, anxiety, or fear. If the sudden onset of a seizure is triggered by a stressful event, you should seek immediate medical attention to avoid complications from these symptoms.
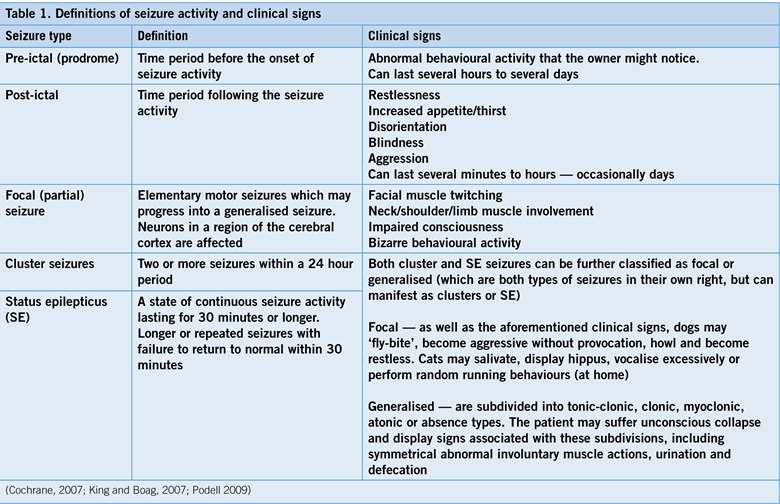
Seizures that are accompanied by loss of consciousness may occur suddenly or gradually progress
Generally, a seizure starts gradually and becomes more severe over time. The number of seizures will increase dramatically if you don't take precautions.
If your doctor diagnoses probable or possible seizures, he or she will start by monitoring your physical and mental status to see how you're feeling and if you're likely to have a seizure. A health care provider will also ask you about symptoms you're experiencing and may ask you to describe your seizures and your feelings and emotions. You'll likely be required to have a physical exam to rule out any health issues.
Your doctor may also conduct neurological tests to rule out any causes of seizures. This includes X-rays, blood tests, and ECG. If there's no medical cause for your seizures, he or she may prescribe a type of drug called a benzodiazepine that can be used to treat the symptoms of the seizures.
When a doctor determines that you're having a seizure, he or she will usually give you medicines to help reduce the seizure symptoms and reduce the risk of seizures recurring. Medications used to treat seizures include anticonvulsants such as Diazepam; antipsychotic drugs, such as Olanzapine andolanzeprum; sedatives like Flunitrazolam; and antidepressants, like Neurontin.
Many people choose to take epilepsy medications as soon as they're diagnosed with seizures because these medications are less expensive than hospitalization and can often be taken for months or years. Even though epilepsy medications can be helpful in dealing with seizures, they cannot prevent seizures from happening again, and some medications may be addictive.
If you're suffering from seizures, it's important to continue taking seizure medications for a long time. It's also important to remember to avoid alcohol and caffeine. These can make seizures worse and may increase the likelihood of an absence seizure.
If you're concerned that you may have an absence seizure, contact your health care provider right away. There may be some medications or combinations of medications you could be taking that could trigger the seizure or may worsen the condition.