
Emg is an abbreviation for Electroencephalograph, an imaging technique used to detect the frequency, amplitude, and direction of electrical activity in the brain. EMG testing and nerve conduction studies (NCS) are clinical neurophysiological tools used to assess brain function and disease. These tests are the main diagnostic tools for neuropsychiatric clinical neurophysiological research, a specialized field of clinical neurophysiology.
Nerve Conduction Study, also called NCS, is an imaging technique that involves inserting a catheter into the carotid artery. After the catheter is inserted, a transmitter is attached to the end of the catheter. The device sends a small amount of electrical stimulation to the brain. When stimulation occurs, the brain will produce electrochemical signals in the form of waves that can be picked up by electrodes in the NCS machine.
EEG or electroencephalograph is another common method used to measure brain activity. The basic principle of this technique is based on electroencephalography. Electrodes on the scalp are placed in the area of the brain that is measured by electroencephalography. During this procedure, electrical signals are read from neurons by electrodes.
Emg testing is used to determine if a patient has seizures. A device called an electrocardiogram is also used to diagnose heart disease, arrhythmias, and heart valve disease. In fact, most patients do not require an invasive procedure, such as EMG testing, if their symptoms match those of another condition.
For EMG testing, electrodes are placed on specific areas of the body. EMG electrodes are placed on the patient’s arm or back so that the electrical activity of the muscles in the body can be measured. Muscle contraction is usually the result of voluntary or involuntary movement, and the EMG signal helps the doctor determine the type of muscle contraction. The EMG signals are then interpreted by the computer. This information is then used to help the doctor determine the cause and extent of the patient’s symptoms.
In the NCS, electrodes are placed on specific muscle groups of the patient’s body to determine muscle tone. Muscle tone affects blood flow and allows muscles to stretch and relax during a variety of activities. For example, if the patient is suffering from stress, this will relax certain muscles. If a muscle is tense, it will not only relax; it will also cause an increase in blood flow.
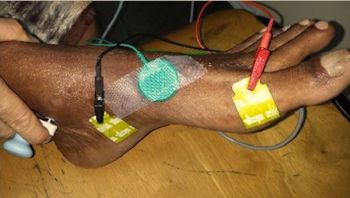
During the EMG test, muscle contraction is recorded on a computerized trainer. As a result, the EMG signal is used to determine the amount of fluid and the rate of muscle contraction. In addition, the EMG signals are compared with the patient’s previous actions to determine how much fluid is being pumped into the arteries and how much is flowing out. Muscle tone is also compared with certain symptoms to help make a diagnosis.
The combination of these two clinical neurophysiological tools can be useful in the diagnosis of many types of diseases. Some of the more common conditions that can be used for diagnosis include: migraine, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), sleep apnea, fibromyalgia, multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, depression, epilepsy, anxiety disorders, brain injury, and epilepsy.
The main limitation of EMG testing is that it cannot detect all of the patient’s symptoms. You may need to use other tests to confirm that the EMG test is accurate for detecting symptoms of a particular condition. In addition, EMG testing is not always reliable because the patient may not respond to stimulation of the test.
There are many forms of EMG testing available today. These range from simple one-way electrocardiograms, which measure the heart rate and electrical activity of muscle cells in the heart, to electroencephalographs, which measure a patient’s brain waves, and magnetic resonance imaging tests, which examine the brain’s brain activity.
Performing an EMG correctly can help improve the diagnosis of many different conditions. However, it is important for patients to understand that EMG is not a substitute for a physician’s examination.