Pseudomonas aeruginosa is a naturally occurring bacterium that causes infection in the digestive tract.
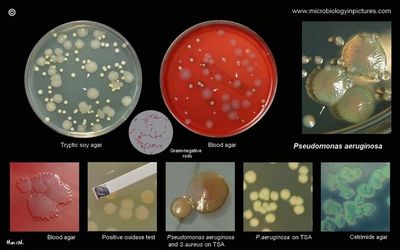
It is anaerobic, meaning it lives in a low oxygen environment and can live in the absence of oxygen. When it infects an individual, the infection spreads to other areas of the body, usually the lungs and the bloodstream.
P. aeruginosa is responsible for approximately one third of hospital stays for people who have pneumonia. When this bacterium grows out of control, it produces symptoms such as severe abdominal pain and diarrhea. There are a few common forms of Pseudomonas, but it is the more aggressive forms that are the leading cause of death worldwide.
The most serious form of Pseudomonas is septicemia, or sepsis. This is a blood disease caused by infection with Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Septicemia occurs when bacteria from the urinary tract to multiply out of control. When the bacteria are able to travel into the bloodstream, they can travel to the lungs and the brain, causing symptoms including seizures, coma, and death.
The second leading form of Pseudomonas is bacteremia.
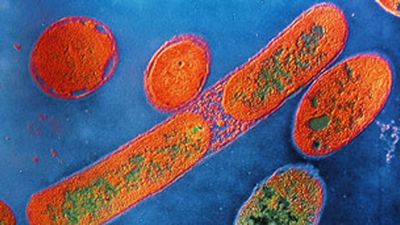
This is caused when Pseudomonas aeruginosa builds up in the body’s tissues and organs. The bacteria can produce toxins that can interfere with the normal functions of the organs, causing symptoms such as abdominal pain, heart failure, liver failure, and shock.
The third form of Pseudomonas is an infection that occurs in the intestines. This is called enteritis and it occurs when an individual has an intestinal infection and the individual’s bowels become blocked. The condition becomes so severe that the person becomes unable to digest and absorb food properly, and the bacteria in their intestines produce toxins that damage the tissue.
The fourth form of Pseudomonas is a condition that occurs when an individual is colonized by other forms of Pseudomonas. These types include those that occur in other areas of the body such as the skin and can spread throughout the body through the air, as well as other body fluids such as the mouth, sweat, and urine. In order to eliminate these bacteria, the individual must be treated by a doctor.
Once a patient begins treatment, the goal of treatment for P. aerugillomatosis is to kill off all the Pseudomonas bacteria. This will often include antibiotic medications and sometimes it will also involve the use of a surgical procedure such as Diflucan.
There are a number of treatments available for P. aeruginosa, but all of them are aimed at helping to kill off the bacteria that causes the infection so that it cannot reproduce.
The bacteria will also be removed from the affected area.
Antibiotics. These treatments will help to eliminate all the bacteria that cause the problem, and the patient will be given a course of antibiotics.
A surgical procedure is required if the patient requires a more aggressive type of antibiotic. Surgical procedures can be performed in an outpatient setting, or in a hospital. Some of the invasive and more serious surgeries will be performed in the hospital, such as endoscopic surgery.
Other than surgery, a course of antibiotics is not necessary for long-term treatment. Most doctors will prescribe anti-biotic drugs for short-term treatments.
Immune System Boosters. Immune system boosters have also been found to be very useful for treating Pseudomonas. Doctors will prescribe this medication if patients have weakened immune systems and are experiencing repeated bouts of P. aeruginosa.
If you are not in good health conditions, the best treatment option is to seek medical attention. If you or a loved one is sick, you should contact your doctor immediately.