Tetanus, also known as lockjaw, is an infectious bacterial infection that affects the upper respiratory tract.

The bacteria can enter through cuts, deep penetrations or punctures such as those made by sharp objects like knives or nails. However, the most common way to contract this disease is through a bite or wound, usually made by a tick or flea.
It can affect anyone, regardless of their age, race, gender, health status, history, or immunity, and it begins with an inflammation of the respiratory system brought on by infection with a bacterium called Toxocara canis. Toxocara canis is an obligate anaerobe, which means it cannot survive without air or other conditions conducive to it. This bacterium invades the body’s tissues and bloodstream and resides in small pockets. When infected, the bacterium produces a spirochete (toxoid) to destroy muscle cells and organs. This causes the characteristic signs of lockjaw, including loss of muscle control, breathing difficulties, convulsions, and weakness.
Because the lungs and muscles are the first to be affected, tetanus affects any organ that receives blood from the lung or from the skeletal muscle. This may include the heart, kidney, liver, spleen, spleens, and the central nervous system, including the brain and nervous trunk. When these organs are affected, the victim will start to lose consciousness. While unconscious, the victim may develop seizures, tremors, or convulsions.
Lockjaw may also affect the spinal cord, leading to paralysis of the cord and brain damage. At the same time, because the muscles of the face and mouth contract, the victim may also experience choking sensations. The person can experience these symptoms until he wakes up and can breathe on his own.
While a more serious case of tetanus can result in death, most of the people affected by this disease recover completely. A mild case can be treated using antibiotics or an anti-parasitic medication.
In most cases, doctors begin with a medical examination at the local poison center. to rule out other diseases, but they also do a series of blood tests to identify the bacteria causing the infection.
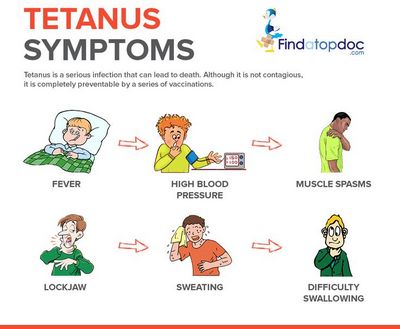
Once the diagnosis is made, the doctor can administer treatment through topical or oral medications depending on the cause of the infection. Some people, especially children, might need to undergo surgery.
Oral medications include antihistamines, decongestants and nasal sprays. Steroids are used to reduce inflammation. In severe cases, oxygen therapy is administered. A surgical option is to remove the infected organ.
The good news about tetanus is that it is curable and usually not fatal. The bad news is that there is no known cure. But, with early treatment, you are less likely to suffer permanent damage.
It is also important to remember that there is no cure, so it is important to seek prompt treatment if you suspect that you are suffering from tetanus. It is also important to note that children have a higher chance of being affected by this disease than adults. As a matter of fact, the chances of a child becoming infected with tetanus are twice as high as the chances of an adult.
There are various treatment options available for treatment of tetanus. If your doctor suggests surgery, the decision should be made based on the severity of the case. In some cases, the only way to avoid surgery is if the symptoms are severe.
In most cases, local poison centers provide treatment for patients. These centers may offer antibiotics and decongestants for immediate relief of symptoms, but most cases can be cured without these measures.
In severe cases, the patient may have to stay in the hospital for days or even weeks. So, it is important to seek prompt treatment as soon as possible.