Serotonin-related substances are neurotransmitters found in the central nervous system of vertebrates.
Serotonin is a major neurotransmitter, and its biological function is multifaceted and complex, regulating mood, cognition, motivation, learning, memory, and several other physiological functions such as vasoconstriction and vomiting. The serotonin molecule is present in various brain areas, particularly the central nervous system and is primarily involved in regulating mood. Serotonin levels are usually high during times of happiness and well-being, but they drop when the body is under stress. In other words, serotonin acts as a mood stabilizer.
Serotonin and seratonin are two different types of serotonergic neurotransmitters. Serotonin, or 5-HT, is an important component of the human brain and is found to affect the function of most neurons, including those in the brain. Serotonin can be produced in the brain by means of the nerve cells called neurons and released into the bloodstream via the serotonin transporter protein. The receptor on the serotonin transporter is responsible for releasing serotonin.
Serotonin and seratonin are both secreted into the bloodstream from the serotonergic neurons. The amount of serotonin and seratonin secreted varies with different people, and it may vary within the body as well. However, serotonin and seratonin are considering to be metabolized into inactive compounds by the liver, which are then excreted through the urine.
Serotonin and seratonin have numerous functions, including regulation of blood sugar, metabolism, cardiovascular activity, gastrointestinal processes, and immune and neuroendocrine function. They are also important to bone development, growth, and puberty.
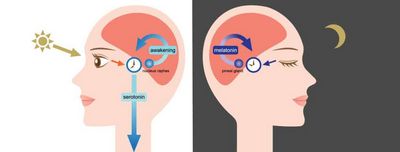
Serotonin and seratonin also regulate sleep and wakefulness. Seratonin is secreted before sleep to initiate the sleep-wake cycle and induce sleep. Serotonin, on the other hand, is secreted during the day to stimulate arousal and promote sleep. Serotonin can prevent the release of melatonin, which is the main hormone that controls the pineal gland’s production of melatonin.
Serotonin and seratonin are also involved in learning and memory processes. Serotonin is one of the neurotransmitters that are primarily responsible for the storage of information in the brain, while melatonin is primarily responsible for the production of information on the retina.

in the brain. The ability of serotonin to bind to the receptor sites on the serotonin transporter protein can prevent the re-uptake of melatonin in the brain, preventing it from being excreted in the bloodstream.
Serotonin and melatonin both play roles in regulating the immune system. They inhibit the replication of some viruses and increase the effects of some anti-viral drugs. Serotonin also helps to suppress the effects of inflammatory cytokines, which are involved in inflammation and the regulation of immunity. Seratonin has been found to enhance memory and the ability of the immune system.
Serotonin and seratonin also affect the process of sexual arousal, and both help in the formation of the semen. A number of neurotransmitters are involved in the secretion of sex hormones.
Serotonergic neurons transmit signals between brain cells. These cells produce serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates feelings of pleasure, appetite, sleep and mood. Serotonin levels are also affected by many environmental factors, such as exercise, food intake, and exercise.
The decrease in serotonin levels in patients with major depression and anxiety is associated with the occurrence of hallucinations, delusions, irritability, depression, and suicidal thoughts. In these instances, medications containing serotonin antagonists are used to counteract the negative affects of these chemicals. Although serotonin is thought to have an antidepressant effect, the medications often produce unpleasant side effects, such as nausea and vomiting.
Other non-serotonin-based medications are available, but often they have undesirable side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, constipation, dizziness, confusion, and drowsiness. It is sometimes difficult to treat depression and anxiety with antidepressants because of the risk of rebound depression. In addition to serotonin-based drugs, there are anti-seizure medicines that lower the level of serotonin in the brain. If the level of serotonin is reduced in the brain, the nervous system produces more serotonin to control brain activity.
Serotonin and seratonin have been shown to slow the aging process by increasing cellular regenerating activity, and thus slowing down the aging process. Serotonin and seratonin may be responsible for delaying the onset of Alzheimer’s disease and reducing the incidence of depression and heart attack.